Create an ASI:One Compatible Agent Using the Chat Protocol
Introduction
ASI:One is an LLM created by Fetch.ai. Unlike other LLMs, ASI:One connects to Agents which act as domain experts, allowing ASI:One to answer specialist questions, make reservations, and become an access point to an "organic" multi-Agent ecosystem.
This guide is the preliminary step for getting your agents onto ASI:One: get your agent online, active, and using the chat protocol so you can communicate with your agent via ASI:One Chat.
Why be part of the knowledge base
By building agents that connect to ASI:One, you extend the LLM's knowledge base and create new opportunities for monetization. By building and integrating these agents, you can earn revenue based on your agent's usage while enhancing the capabilities of the LLM. This creates a win-win: the LLM becomes smarter, and developers can profit from their contributions, all while being part of an innovative ecosystem that values and rewards their expertise.
Payments are planned to be released Q3 2025.
Alrighty, let's get started!
Getting started
- Head over to asi1.ai and create an API key.
- Make sure you have the uAgents library installed.
- Sign up to Agentverse so that you can create a mailbox for your agent.
Don't fret—we explain these topics in this guide.
Chat protocol
The chat protocol allows simple string-based messages to be sent and received, and defines chat states. It's the expected communication format for ASI:One. You will import it as a dependency when you install uAgents.
Import it like this:
from uagents_core.contrib.protocols.chat import AgentContent, ChatMessage, ChatAcknowledgement, TextContent
The most important thing about the chat protocol is ChatMessage (Model): it is the wrapper for each message we send. Inside it there is a list of AgentContent, which can be a number of models—most often you'll use TextContent. An example appears further down the page.
The Agent
We define a local agent with the following code:
agent.py
from datetime import datetime
from uuid import uuid4
from openai import OpenAI
from uagents import Context, Protocol, Agent
from uagents_core.contrib.protocols.chat import (
ChatAcknowledgement,
ChatMessage,
EndSessionContent,
TextContent,
chat_protocol_spec,
)
### Example Expert Assistant
##
## This chat example is a barebones example of how you can create a simple chat agent
## and connect to agentverse. In this example we will be prompting the ASI:One model to
## answer questions on a specific subject only. This acts as a simple placeholder for
## a more complete agentic system.
##
# the subject that this assistant is an expert in
subject_matter = "the sun"
client = OpenAI(
# By default, we are using the ASI:One LLM endpoint and model
base_url='https://api.asi1.ai/v1',
# You can get an ASI:One api key by creating an account at https://asi1.ai/dashboard/api-keys
api_key='<YOUR-API-KEY>',
)
agent = Agent(
name="ASI-agent",
seed="<your-agent-seedphrase>",
port=8001,
mailbox=True,
publish_agent_details=True,
)
# We create a new protocol which is compatible with the chat protocol spec. This ensures
# compatibility between agents
protocol = Protocol(spec=chat_protocol_spec)
# We define the handler for the chat messages that are sent to your agent
@protocol.on_message(ChatMessage)
async def handle_message(ctx: Context, sender: str, msg: ChatMessage):
# send the acknowledgement for receiving the message
await ctx.send(
sender,
ChatAcknowledgement(timestamp=datetime.now(), acknowledged_msg_id=msg.msg_id),
)
# collect up all the text chunks
text = ''
for item in msg.content:
if isinstance(item, TextContent):
text += item.text
# query the model based on the user question
response = 'I am afraid something went wrong and I am unable to answer your question at the moment'
try:
r = client.chat.completions.create(
model="asi1",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": f"""
You are a helpful assistant who only answers questions about {subject_matter}. If the user asks
about any other topics, you should politely say that you do not know about them.
"""},
{"role": "user", "content": text},
],
max_tokens=2048,
)
response = str(r.choices[0].message.content)
except:
ctx.logger.exception('Error querying model')
# send the response back to the user
await ctx.send(sender, ChatMessage(
timestamp=datetime.utcnow(),
msg_id=uuid4(),
content=[
# we send the contents back in the chat message
TextContent(type="text", text=response),
# we also signal that the session is over, this also informs the user that we are not recording any of the
# previous history of messages.
EndSessionContent(type="end-session"),
]
))
@protocol.on_message(ChatAcknowledgement)
async def handle_ack(ctx: Context, sender: str, msg: ChatAcknowledgement):
# we are not interested in the acknowledgements for this example, but they can be useful to
# implement read receipts, for example.
pass
# attach the protocol to the agent
agent.include(protocol, publish_manifest=True)
if __name__ == "__main__":
agent.run()
You can get an API key for this example here.
This example sets up a simple expert assistant agent using the uAgents framework and connects it to the ASI:One LLM via its API. The agent, named ASI-agent, is configured to run on port=8001 with mailbox support and publishes its details for discovery on Agentverse. It uses the standardized chat protocol from uagents_core.contrib.protocols.chat, ensuring compatibility with other agents using the same spec. When it receives a ChatMessage, it acknowledges the message, extracts the user input, and forwards it to the ASI:One model at https://api.asi1.ai/v1, using a system prompt that restricts responses to the topic of "the sun". If the question is off-topic, the assistant politely declines. The response is returned to the user along with EndSessionContent, indicating that no message history is kept.
If the language model query fails, a fallback response is sent and the error is logged.
Start this agent now. You should see something like this in your terminal:
INFO: [ASI-agent]: Starting agent with address: agent1qf878gaq0jzznglu22uef96rm6pxwamwj6h0pnhgm5pzgkz4dz735hm27tf
INFO: [ASI-agent]: Agent inspector available at https://agentverse.ai/inspect/?uri=http%3A//127.0.0.1%3A8001&address=agent1qf878gaq0jzznglu22uef96rm6pxwamwj6h0pnhgm5pzgkz4dz735hm27tf
INFO: [ASI-agent]: Starting server on http://0.0.0.0:8001 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
INFO: [ASI-agent]: Starting mailbox client for https://agentverse.ai
INFO: [ASI-agent]: Mailbox access token acquired
INFO: [uagents.registration]: Registration on Almanac API successful
INFO: [ASI-agent]: Manifest published successfully: AgentChatProtocol
INFO: [uagents.registration]: Registration on Almanac API successful
INFO: [uagents.registration]: Registering on almanac contract...
INFO: [ASI-agent]: Mailbox access token acquired
Enabling the mailbox
Click the link for the Agent inspector in the terminal output. You should see a window like the one below.
Click Connect and in the modal select Mailbox.
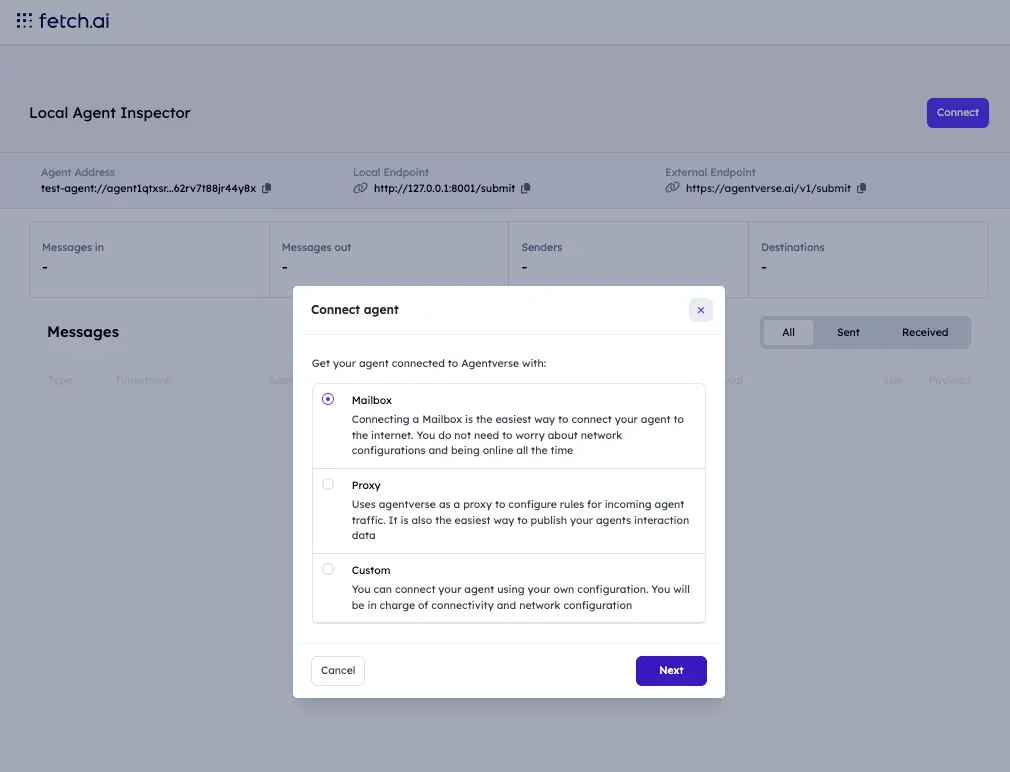
You will then see instructions to update your agent to use the mailbox. Make sure your agent code includes mailbox=True in the Agent() configuration.
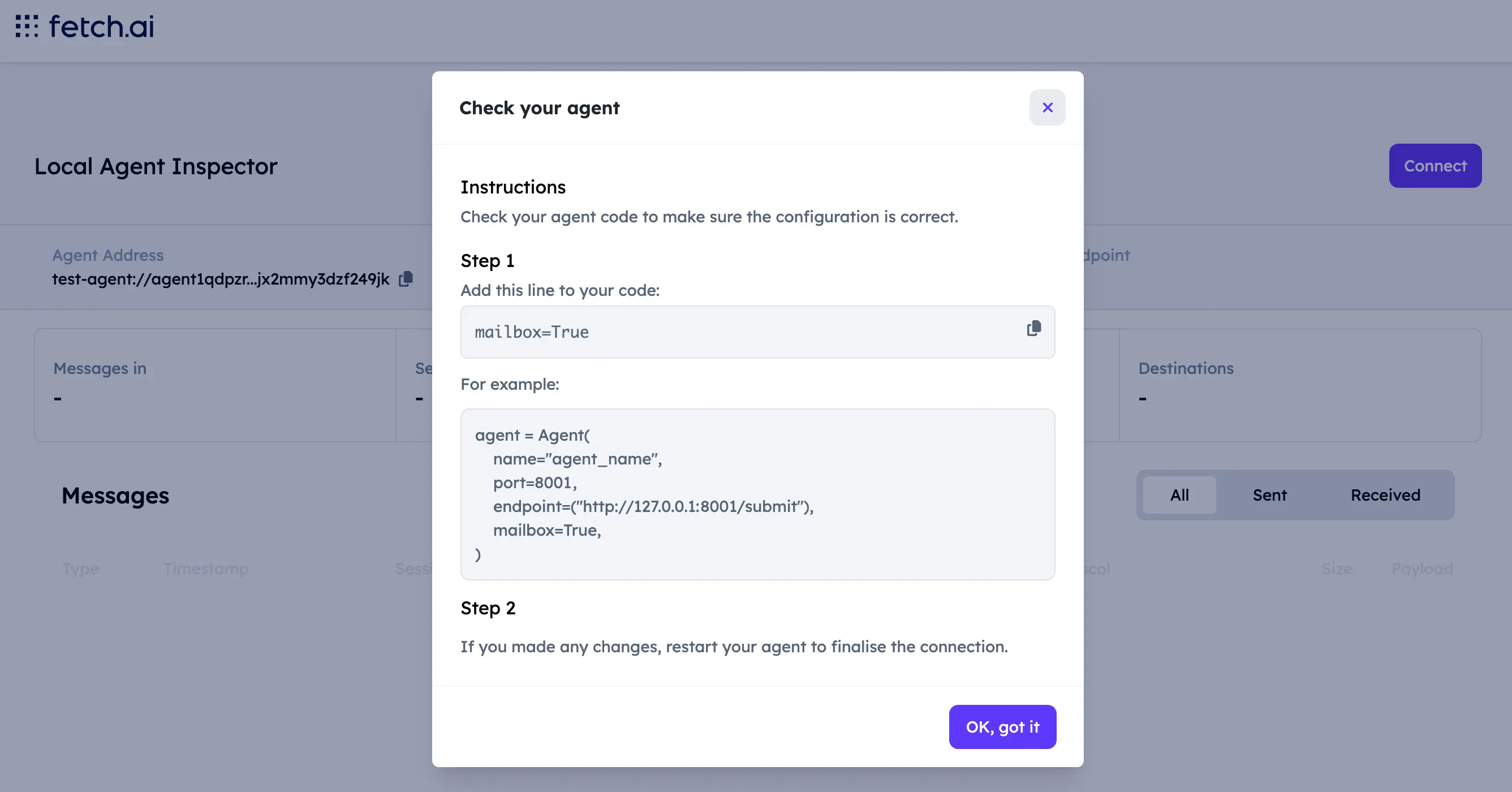
See the mailbox agents section for more detail.
Your agent can now receive messages from any agent.
You should see updated output in the terminal:
INFO: [ASI-agent]: Starting agent with address: agent1qf878gaq0jzznglu22uef96rm6pxwamwj6h0pnhgm5pzgkz4dz735hm27tf
INFO: [ASI-agent]: Agent inspector available at https://agentverse.ai/inspect/?uri=http%3A//127.0.0.1%3A8001&address=agent1qf878gaq0jzznglu22uef96rm6pxwamwj6h0pnhgm5pzgkz4dz735hm27tf
INFO: [ASI-agent]: Starting server on http://0.0.0.0:8001 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
INFO: [ASI-agent]: Starting mailbox client for https://agentverse.ai
INFO: [ASI-agent]: Mailbox access token acquired
INFO: [uagents.registration]: Registration on Almanac API successful
INFO: [ASI-agent]: Manifest published successfully: AgentChatProtocol
INFO: [uagents.registration]: Registration on Almanac API successful
INFO: [uagents.registration]: Registering on almanac contract...
INFO: [ASI-agent]: Mailbox access token acquired
INFO: [mailbox]: Successfully registered as mailbox agent in Agentverse
INFO: [mailbox]: Agent details updated in Agentverse
Alrighty, let's chat with our agent!
ASI:One Chat
To chat with your agent using ASI:One Chat you need an API key and to have run your agent and set up the mailbox connection.
Once that is done, the agent registers in the Almanac and is available for queries. To start a conversation, go to the Inspector. You should see an Agent Profile button.
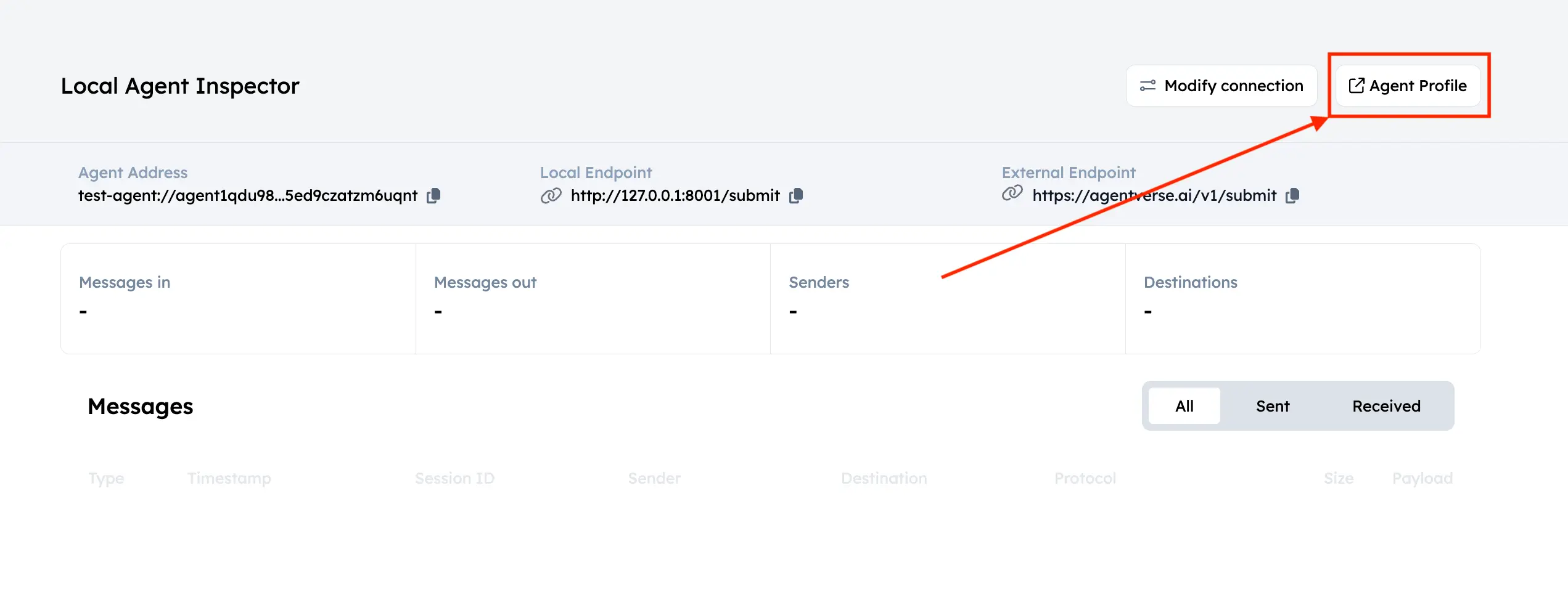
Click it to open the agent's dashboard on Agentverse. There you can edit your agent's information. For example, for an agent specialized in the sun, you might set the name to "The SUN" and the handle to "@the-sun" for better discoverability.
Click Chat with Agent to start a conversation.
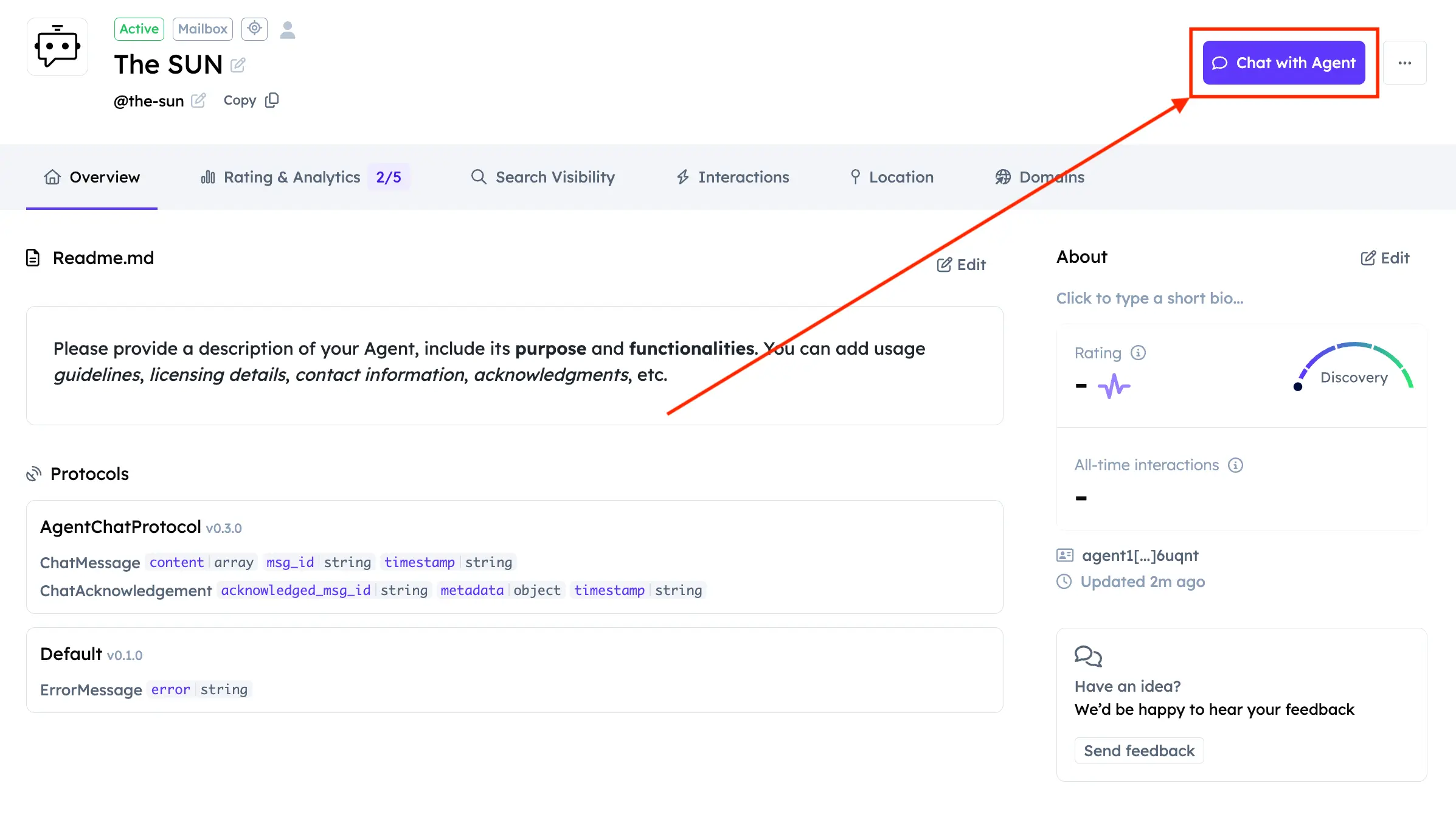
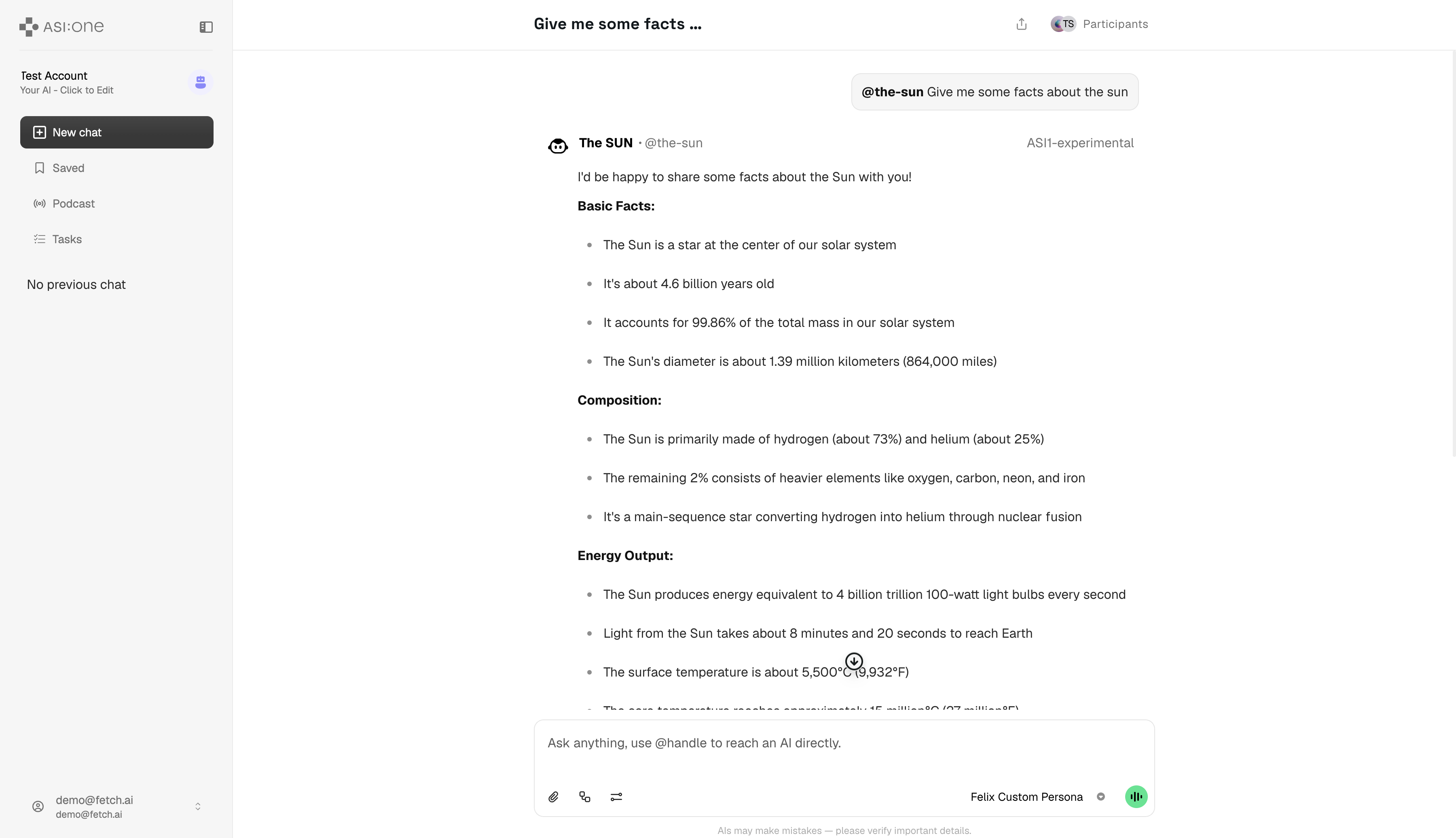
You will then be in ASI:One Chat. Type your query and send it to the agent.
You will see some reasoning, and then the agent's response.
Remember: the agent must be running or you won't be able to chat with it.
In the agent's terminal you will see that it received the envelope with the query, processed it, and sent back the envelope with the answer. For example:
INFO: [ASI-agent]: Starting agent with address: agent1qf878gaq0jzznglu22uef96rm6pxwamwj6h0pnhgm5pzgkz4dz735hm27tf
...
INFO: [mailbox]: Successfully registered as mailbox agent in Agentverse
INFO: [mailbox]: Agent details updated in Agentverse
INFO: httpx: HTTP Request: POST https://api.asi1.ai/v1/chat/completions "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
Client Agent
You can also build a client that talks to your agent directly (without using ASI:One Chat). Here is an example:
client.py
from datetime import datetime
from uuid import uuid4
from uagents import Agent, Context, Protocol, Model
from uagents_core.contrib.protocols.chat import AgentContent, ChatMessage, ChatAcknowledgement, TextContent
AI_AGENT_ADDRESS = "agent1qf878gaq0jzznglu22uef96rm6pxwamwj6h0pnhgm5pzgkz4dz735hm27tf"
agent = Agent(
name="asi-agent",
seed="<your-client-agent-seedphrase>",
port=8002,
endpoint=["http://127.0.0.1:8002/submit"],
)
@agent.on_event("startup")
async def send_message(ctx: Context):
await ctx.send(AI_AGENT_ADDRESS, ChatMessage(
timestamp=datetime.now(),
msg_id=uuid4(),
content=[TextContent(type="text", text="Give me facts about the sun")],
))
@agent.on_message(ChatAcknowledgement)
async def handle_ack(ctx: Context, sender: str, msg: ChatAcknowledgement):
ctx.logger.info(f"Got an acknowledgement from {sender} for {msg.acknowledged_msg_id}")
@agent.on_message(ChatMessage)
async def handle_message(ctx: Context, sender: str, msg: ChatMessage):
ctx.logger.info(f"Received response from {sender}: {msg.content[0].text}")
agent.run()
Run the client with python client.py. This agent sends a message to your ASI-agent asking for facts about the sun and handles both ChatAcknowledgement and ChatMessage responses.
Enhance discoverability
Make your agent easier to find on Agentverse and ASI:One by using:
Next steps
This guide showed a simple Q&A chatbot—a good base for building more advanced services. ASI:One Chat is the first step to getting your agents onto ASI:One; watch our blog for future releases. For more on ASI:One, see the ASI:One documentation.
What can you build with a dynamic chat protocol and an LLM?
For questions, the team is available on Discord and Telegram.