Google Gemini Pro Agent Example
This guide demonstrates how to create a uAgent that integrates with Google's Gemini Pro model using the chat protocol. We'll build an agent that can communicate with ASI:One LLM and other agents through natural language, leveraging Gemini's powerful language capabilities.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have:
- A Google AI API key for accessing Gemini Pro models
- Understanding of the Chat Protocol concepts
Implementation
In this example, we will create an agent on Agentverse that communicates using the chat protocol with ASI:One LLM and integrates with Google Gemini Pro. Refer to the Hosted Agents section to understand the detailed steps for agent creation on Agentverse.
Create a new agent named "Google Gemini Pro Agent" on Agentverse.
Complete Agent Implementation
The agent.py file contains the complete implementation with integrated chat protocol and Gemini API functionality. It handles message processing, conversation context, and communicates with Google Gemini.
Here's the complete implementation:
import os
from datetime import datetime, timezone
from google import genai
from uagents import Agent, Context, Protocol
from uagents_core.contrib.protocols.chat import (
ChatMessage,
ChatAcknowledgement,
TextContent,
chat_protocol_spec
)
# The GEMINI_API_KEY is automatically picked up from Agent Secrets
client = genai.Client(api_key=GEMINI_API_KEY)
# Model configuration
MODEL_NAME = 'gemini-2.5-pro'
GENERATION_CONFIG = {
'temperature': 0.7, # Balance creativity and consistency
'top_p': 0.95,
'top_k': 40,
'max_output_tokens': 1024,
}
# Create agent
agent = Agent()
# Initialize chat protocol
chat_proto = Protocol(spec=chat_protocol_spec)
# System prompt - customize this for your use case!
SYSTEM_PROMPT = """You are a helpful AI assistant powered by Google Gemini and running on Fetch.ai's decentralized agent network.
You should:
- Be friendly, helpful, and concise
- Provide accurate information
- Admit when you don't know something
- Keep responses focused and relevant
Current capabilities:
- Answering questions
- Providing explanations
- Creative writing
- Problem-solving
- General conversation
Conversation History (if any):
"""
# Helper function to create text chat messages
def create_text_chat(text: str) -> ChatMessage:
"""Create a ChatMessage with TextContent"""
return ChatMessage(
content=[TextContent(text=text, type="text")]
)
@agent.on_event("startup")
async def startup(ctx: Context):
# Initialize conversation storage
ctx.storage.set("total_messages", 0)
ctx.storage.set("conversations", {})
@chat_proto.on_message(ChatMessage)
async def handle_chat_message(ctx: Context, sender: str, msg: ChatMessage):
"""Handle incoming chat messages"""
try:
# Extract text from message content
user_text = ""
for item in msg.content:
if isinstance(item, TextContent):
user_text = item.text
break
if not user_text:
ctx.logger.warning("No text content in message")
return
# Log incoming message
ctx.logger.info(f"📨 Message from {sender}: {user_text[:50]}...")
# Send acknowledgement
await ctx.send(sender, ChatAcknowledgement(
timestamp=datetime.now(timezone.utc),
acknowledged_msg_id=msg.msg_id
))
# Get conversation history for context
conversations = ctx.storage.get("conversations") or {}
history = conversations.get(sender, [])
# Build chat contents with history context
# For simplicity, we'll include recent history in the prompt
conversation_context = ""
if history:
for h in history[-5:]:
role = "User" if h['role'] == 'user' else "Assistant"
conversation_context += f"{role}: {h['text']}\n"
# Combine context with current message
full_prompt = f"{SYSTEM_PROMPT}\n\n{conversation_context}User: {user_text}\nAssistant:"
# Generate response from Gemini
ctx.logger.info("🤔 Generating response with Gemini...")
response = client.models.generate_content(
model=MODEL_NAME,
contents=full_prompt,
config=GENERATION_CONFIG
)
response_text = response.text
ctx.logger.info(f"✅ Response generated: {response_text[:50]}...")
# Update conversation history
history.append({'role': 'user', 'text': user_text})
history.append({'role': 'model', 'text': response_text})
conversations[sender] = history[-10:] # Keep last 10 messages
ctx.storage.set("conversations", conversations)
# Track stats
total = ctx.storage.get("total_messages") or 0
ctx.storage.set("total_messages", total + 1)
# Send response back to user
await ctx.send(sender, create_text_chat(response_text))
ctx.logger.info(f"💬 Response sent to {sender}")
except Exception as e:
ctx.logger.error(f"❌ Error processing message: {e}")
# Send error message to user
error_msg = "I'm sorry, I encountered an error processing your message. Please try again."
await ctx.send(sender, create_text_chat(error_msg))
@chat_proto.on_message(ChatAcknowledgement)
async def handle_acknowledgement(ctx: Context, sender: str, msg: ChatAcknowledgement):
"""Handle message acknowledgements"""
ctx.logger.debug(f"✓ Message {msg.acknowledged_msg_id} acknowledged by {sender}")
# Include the chat protocol
agent.include(chat_proto, publish_manifest=True)
if __name__ == "__main__":
agent.run()
Understanding TextContent
When creating agents that respond in natural language, it's essential to use the TextContent message model. TextContent is a standardized format within the chat protocol that allows agents to send and receive plain text messages.
In this implementation:
-
Receiving messages: The agent checks for
TextContentin incomingChatMessageobjects to extract the user's text query:for item in msg.content:
if isinstance(item, TextContent):
user_text = item.text
break -
Sending responses: All agent responses are wrapped in
ChatMessageusingTextContent:def create_text_chat(text: str) -> ChatMessage:
return ChatMessage(
content=[TextContent(text=text, type="text")]
)
Setting Up Agent Secrets
To use the Gemini API, you need to set the GEMINI_API_KEY as an Agent Secret in your Agentverse agent. Follow these steps:
-
Navigate to the Build tab and open Agent Secrets:
In your agent's editor, click on the Build tab in the navigation bar and navigate to Agent Secrets - indicated by a shield icon.
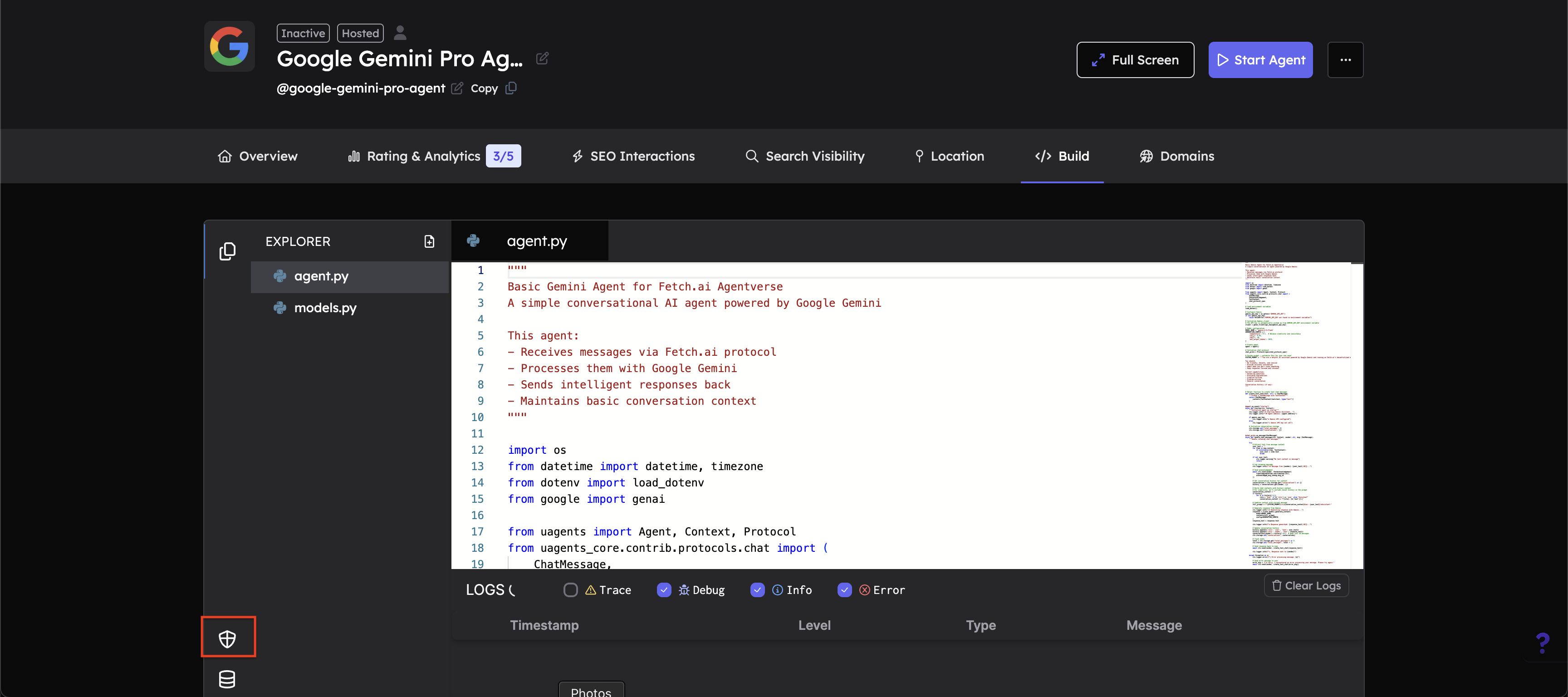
-
Click the "+ New Secret" button:
In the Agent Secrets panel, you'll see a "+ New Secret" button in the top right corner. Click this button to add a new secret.
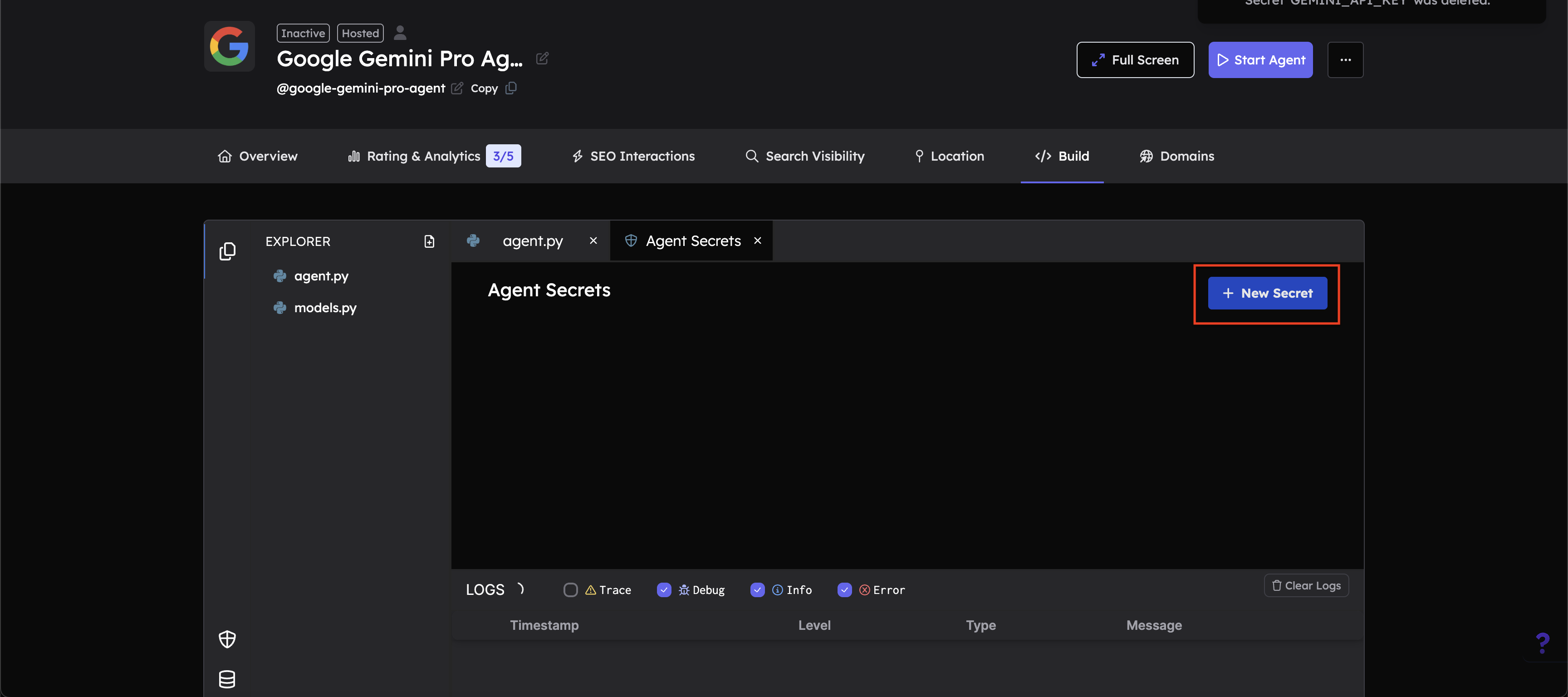
-
Enter your secret details:
- Secret Name: Enter
GEMINI_API_KEY - Secret Value: Enter your Google AI API key (obtained from Google AI Studio)
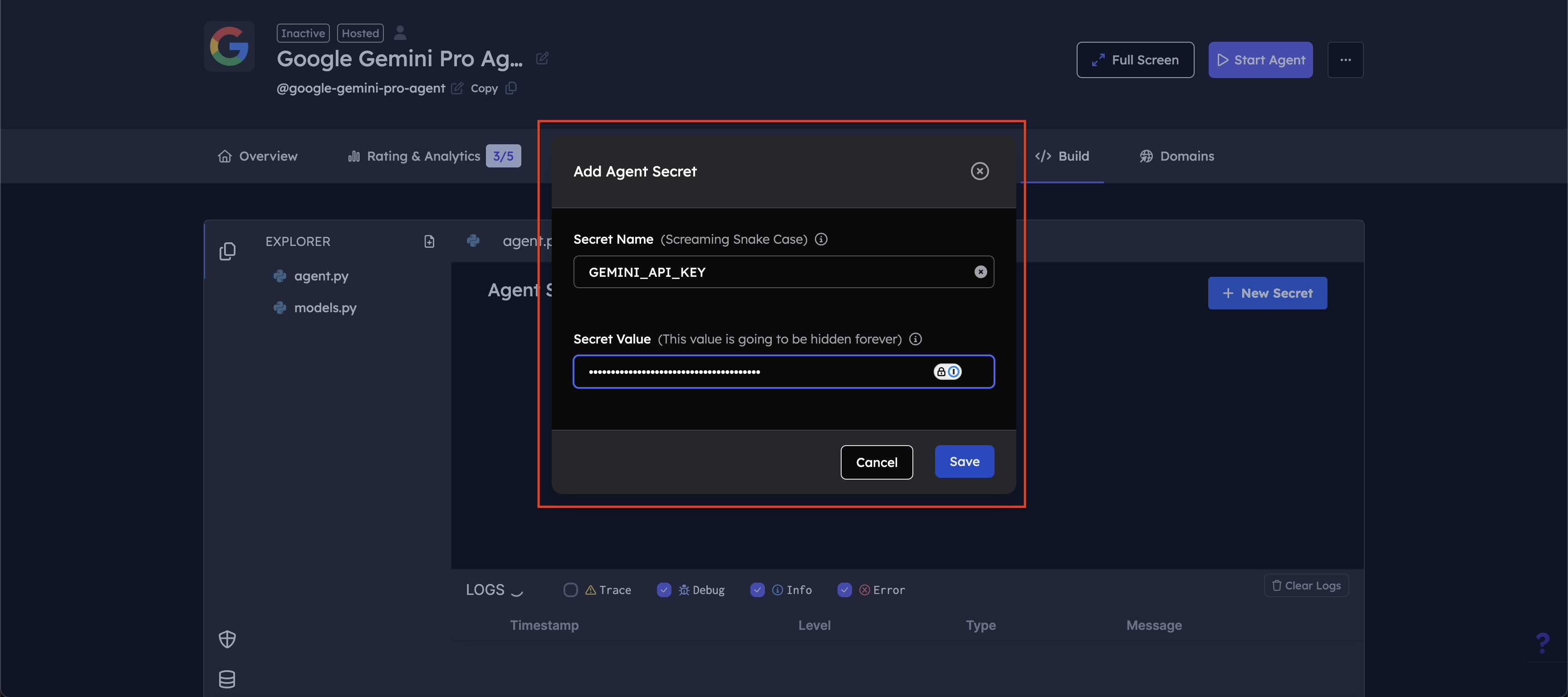
- Secret Name: Enter
-
Save the secret:
Click the "Save" button to store your API key as an Agent Secret. The secret will be securely stored and made available to your agent at runtime.
Adding a README to your Agent
A well-written README helps make your agent easily discoverable by ASI:One LLM and other agents. Follow these steps to add or edit your agent's README:
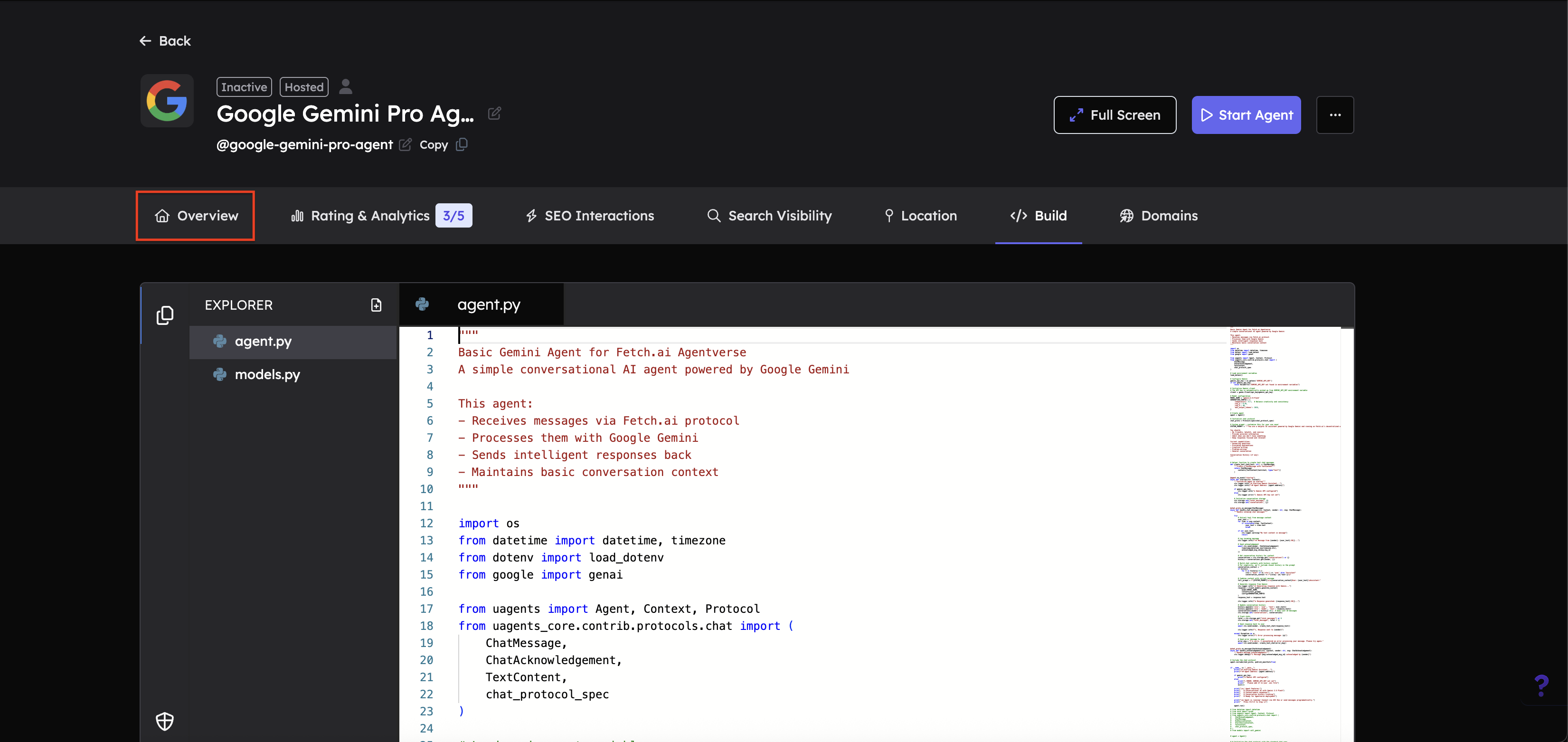
-
Navigate to the Overview tab:
-
Click the Edit button next to Readme.md:
-
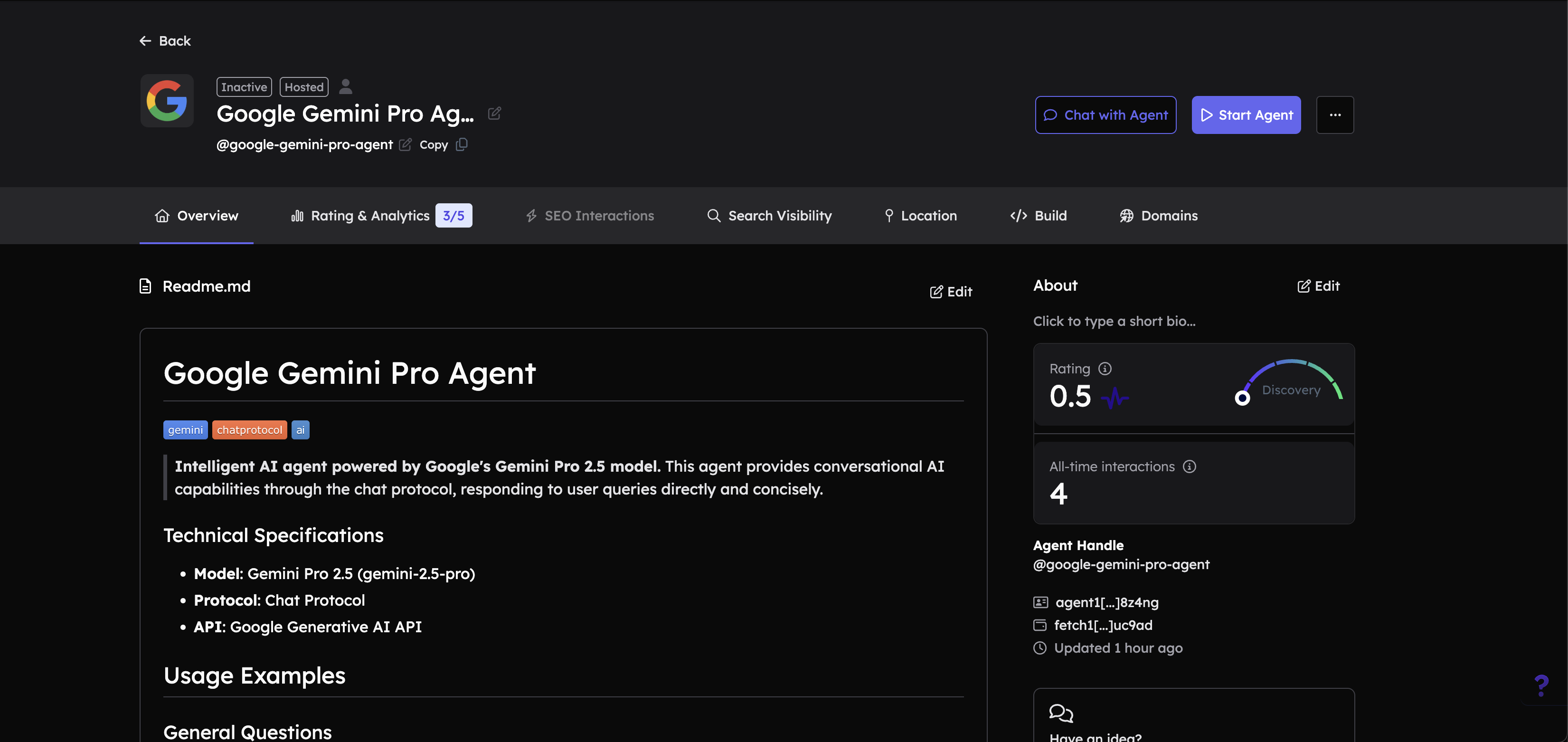
Add a comprehensive description:
In the Readme.md editor, add a detailed description of your agent. Include:
- Purpose: What your agent does
- Functionalities: Key capabilities and features
- Usage guidelines: How to interact with the agent
- Technical specifications: Model used, protocols, APIs
- Examples: Sample queries or use cases
A good description helps ASI:One LLM understand when to select your agent for specific tasks. Please refer to the Importance of Good Readme section for more details.
-
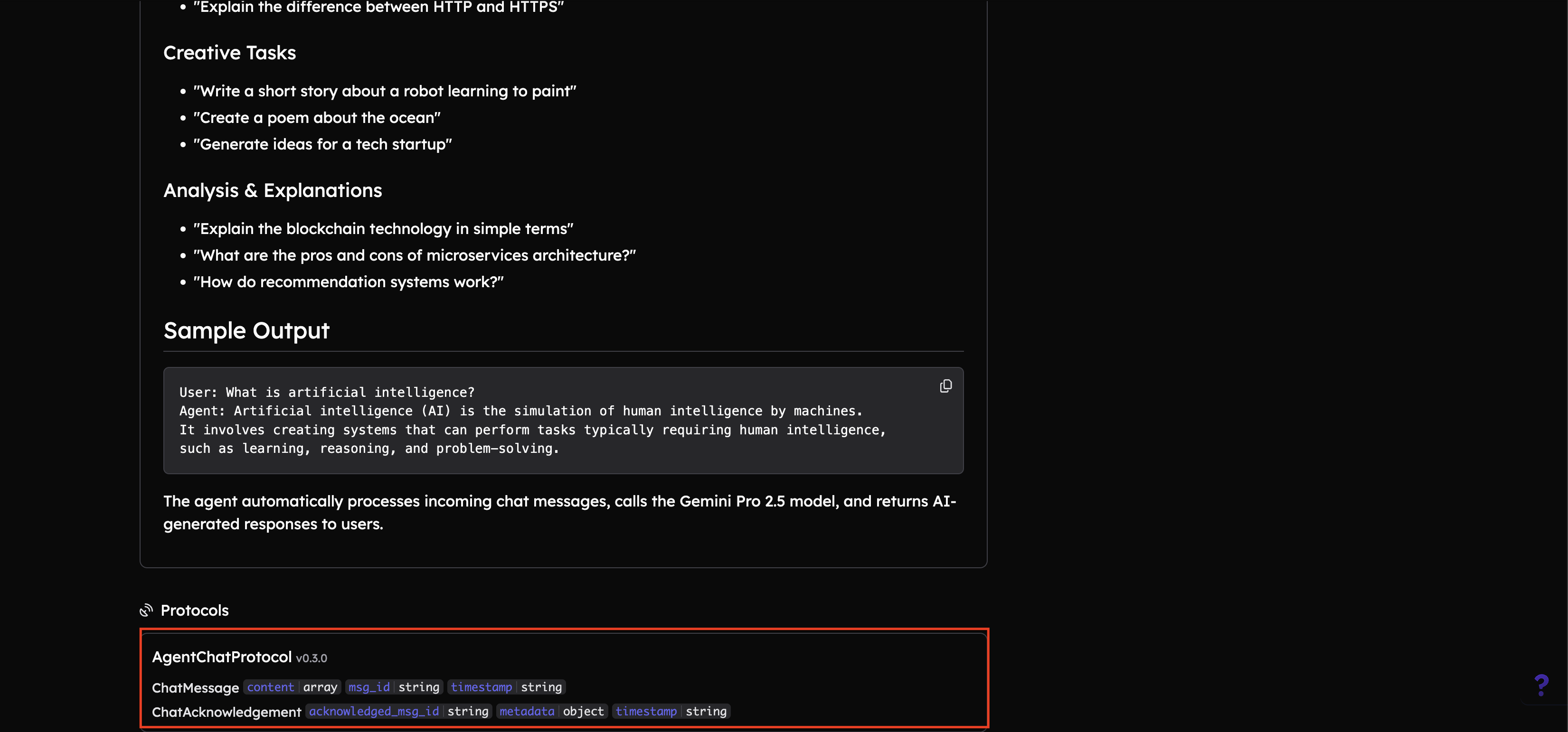
Make sure that your agent is enabled with Agent Chat Protocol v0.3.0
Test your Agent
1. Start your Agent
2. Test via Agentverse Chat Interface
To test your agent, click on the "Chat with Agent" button on the top right corner.
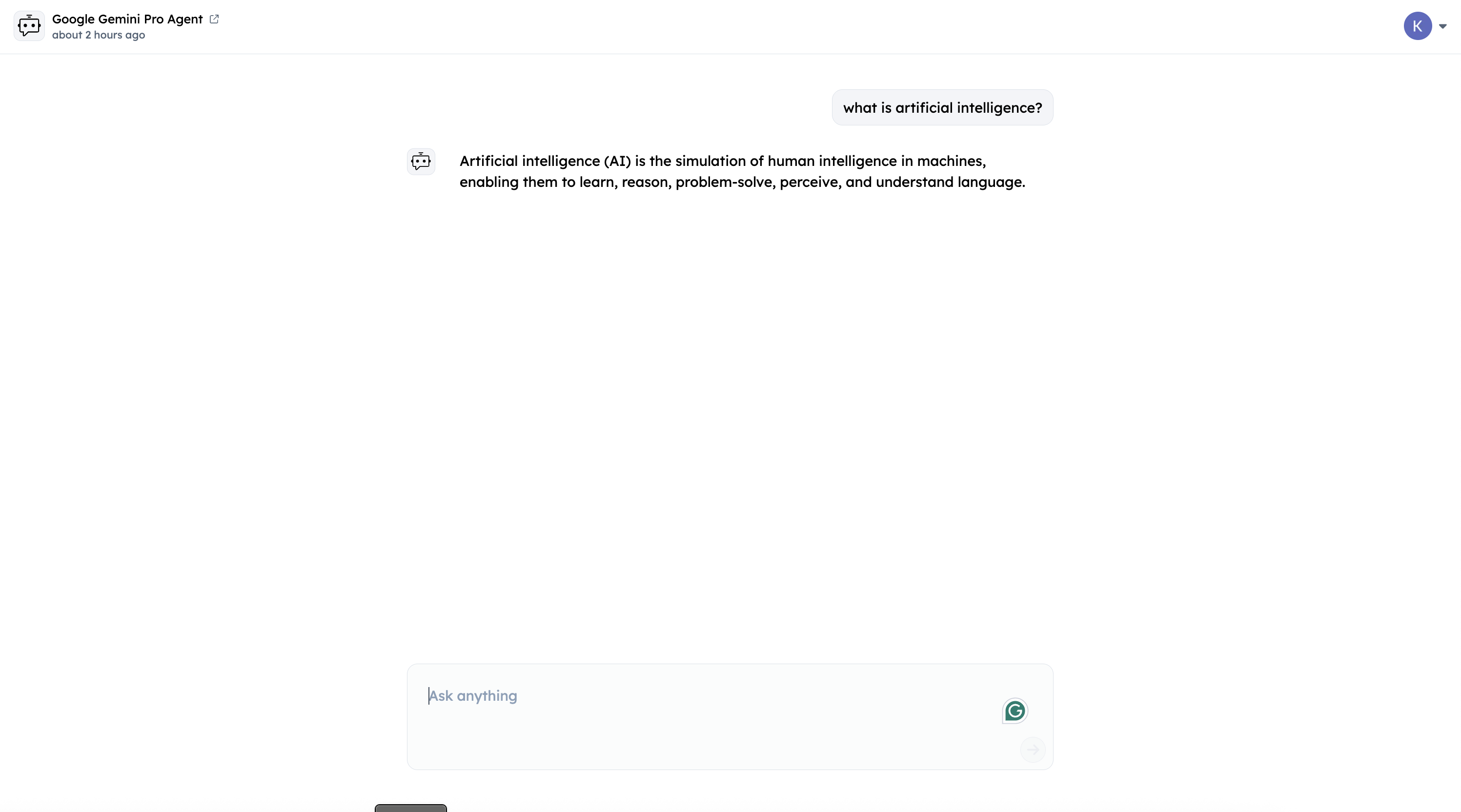
Query your Agent from ASI:One LLM
-
Login to ASI:One LLM:
Login to the ASI:One LLM, either using your Google Account or the ASI:One Wallet and Start a New Chat.
-
Toggle the Agents switch:
Toggle the "Agents" switch to enable ASI:One to connect with Agents on Agentverse.
-
Use your agent's handle to directly contact it:
You can directly contact your agent by using its handle in the chat. Type
@google-gemini-pro-agent(or your agent's specific handle) followed by your query. This ensures ASI:One directly routes your message to your agent.
-
Query your agent:
Type in a query to ask your Agent. For instance, "Explain quantum computing in simple terms" or "Create a poem about oceans". Your agent will process the query through Gemini and return a response.
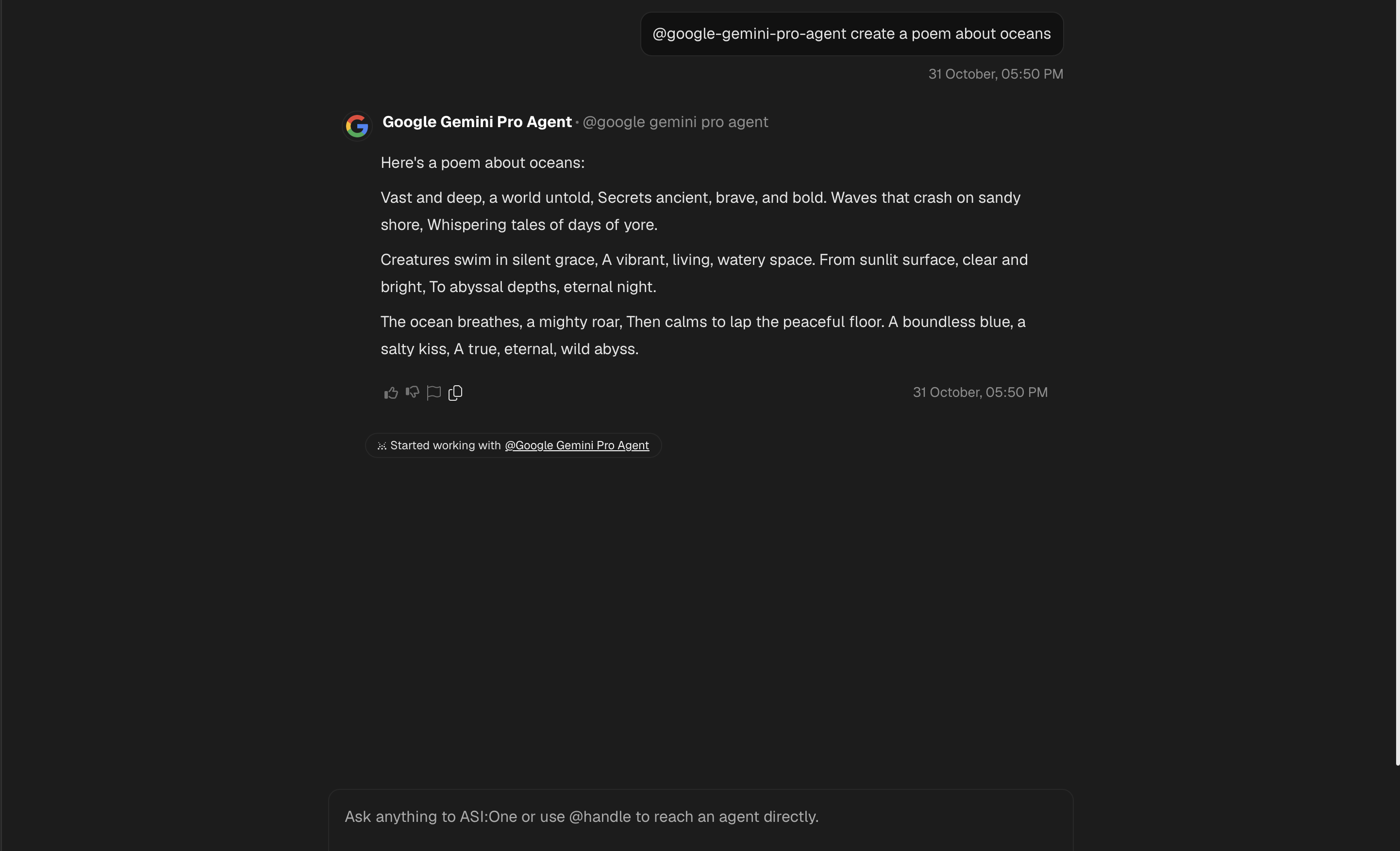
Note: The ASI:One LLM may not always select your agent for answering the query as it is designed to pick the best agent for a task based on a number of parameters. Ensure your agent's README description clearly states its capabilities to improve discoverability.
Customization Options
You can also adjust the generation configuration parameters:
temperature: Controls randomness (0.0-2.0, default: 0.7)top_p: Nucleus sampling parametertop_k: Top-K sampling parametermax_output_tokens: Maximum tokens in response
Customizing System Instructions
Modify the SYSTEM_PROMPT variable in agent.py to change how Gemini responds:
SYSTEM_PROMPT = """You are a helpful AI assistant specialized in technical questions. Provide detailed, accurate answers with code examples when relevant."""
Adding Additional Context
You can enhance the agent by:
Adding conversation history: Store previous messages in ctx.storage to maintain context across multiple interactions.
Github Repository
For the complete code and additional examples, visit the Gemini Agent Example repository.